data analyst gathers, cleans, analyzes, and interprets data to identify patterns, trends, and insights that can inform business decisions. They use various tools and techniques to transform raw data into actionable knowledge, helping organizations make informed decisions.
Key Responsibilities of a Data Analyst:
Data Collection and Preparation:
Gathering data from various sources, cleaning and transforming it to ensure accuracy and consistency.
Data Analysis:
Applying statistical techniques and tools to identify patterns, trends, and relationships within the data.
Data Visualization:
Creating charts, graphs, and dashboards to visually represent data insights and make them easier to understand.
Data Interpretation and Reporting:
Analyzing the findings, drawing conclusions, and presenting them to stakeholders in a clear and concise manner.
Business Problem Solving:
Using data analysis to identify problems, propose solutions, and measure the impact of changes.
Skills and Knowledge Required:
Analytical Skills: The ability to think critically, solve problems, and interpret data effectively.
Statistical Knowledge: Understanding statistical concepts and techniques, such as regression analysis and hypothesis testing.
Programming Skills: Proficiency in programming languages like Python or R to automate data analysis tasks.
Data Visualization Tools: Familiarity with tools like Tableau, Power BI, or Qlik Sense.
Database Management: Knowledge of SQL and relational databases.
Communication Skills: Ability to effectively communicate findings and insights to both technical and non-technical audiences.
Data analysts work in various industries, including:
Business and Finance: Analyzing sales data, marketing campaigns, and financial trends.
Healthcare: Analyzing patient data, medical records, and healthcare trends.
Technology: Analyzing website traffic, social media data, and user behavior.
Government: Analyzing government data, public health data, and economic data. 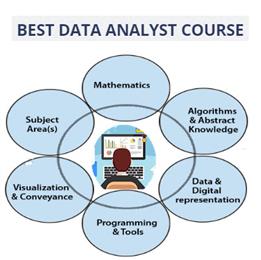
- Teacher: Admin User
